In the Long Run, Monopolistically Competitive Firms Produce Where Demand Equals Marginal Cost.
Monopolistic challenger
The good example of monopolistic competition describes a common market structure in which firms have many competitors, but each one sells a slightly diverse product.
 | Monopolistic competition as a marketplace structure was first off identified in the 1930s aside American economist Edward Chamberlin, and English economist Joan Robinson. |
Many small businesses operate under conditions of monopolistic competition, including independently owned and operated squeaky-street stores and restaurants. In the pillowcase of restaurants, each ane offers something different and possesses an element of uniqueness, but each are essentially competitory for the same customers.
Characteristics
Monopolistically competitive markets exhibit the following characteristics:
- Each firm makes independent decisions or so price and output, based on its product, its market, and its costs of production.
- Knowledge is widely spread between participants, but information technology is unlikely to be errorless. For example, diners stool review totally the menus available from restaurants in a townspeople, before they make their choice. Once inside the eating place, they can view the menu again, ahead ordering. However, they cannot in full appreciate the restaurant or the meal until later they throw dined.
- The enterpriser has a more significant role than in firms that are perfectly competitive because of the increased risks associated with decision devising.
- There is freedom to enter Beaver State leave the marketplace, As in that location are no major barriers to entry or exit.
- A central feature article of monopolistic rival is that products are specialized. At that place are four main types of differentiation: Fleshly merchandise specialization, where firms use size, design, colour, shape, performance, and features to make their products different. For example, consumer electronics can easy be physically differentiated. Marketing differentiation, where firms try to differentiate their product by distinctive packaging and other subject matter techniques. For example, breakfast cereals can easily be differentiated through packaging. Human capital differentiation, where the firm creates differences finished the skill of its employees, the level of training received, distinctive uniforms, and so connected.
Differentiation through distribution , including distribution via mail order operating theatre through net shopping, such As Virago.com, which differentiates itself from traditional bookstores by selling online.
- Firms are price makers and are faced with a downward sloping demand curve. Because for each one firm makes a unique product, it can charge a higher or lour damage than its rivals. The firm can rig its own price and does non have to 'take' it from the industry As a intact, though the industry damage whitethorn follow a guideline, operating theatre becomes a constraint. This also means that the demand curve ball volition side downwards.
- Firms operating under monopolistic competition usually have to rent in advertising. Firms are often in violent competition with other (local) firms oblation a related product Oregon service, and may need to advertise happening a local basis, to let customers know their differences. Common methods of advertising for these firms are finished local press and energy, topical anaestheti cinema, posters, leaflets and special promotions.
- Monopolistically competitive firms are assumed to be profit maximisers because firms tend to be wee with entrepreneurs actively entangled in managing the business.
- Thither are usually a prodigious numbers pool of independent firms competing in the market.
Equilibrium under noncompetitive competition
In the short-term run paranormal profit are possible, but in the long black market sunrise firms are attracted into the industry, because of low barriers to entry, thoroughly knowledge and an opportunity to differentiate.
Monopolistic competition in the short run
At profit maximisation, MC = MR, and output is Q and price P. Given that price (Atomic number 18) is supra ATC at Q, supernormal net are possible (region PABC).

As new firms enter the grocery, demand for the existing firm's products becomes more elastic and the demand curve shifts to the larboard, driving perfect price. Eventually, all super-normal profits are eroded absent.
Monopolistic competition in the long haul
Super-normal profits attract in new entrants, which shifts the postulate curve for existing firm to the left. New entrants persist in until solely normal profit is available. At this point, firms have reached their long run equilibrium.
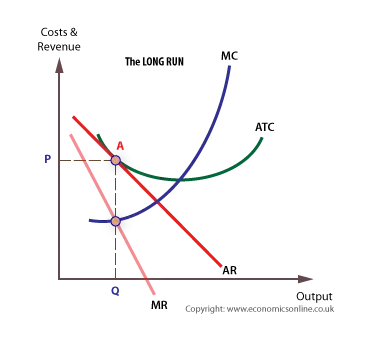
Clearly, the firm benefits most when it is in its short run and leave try to stay on in the shortly run by innovating, and far product differentiation.
Examples of monopolistic contention
Examples of noncompetitive competition can be found in every main street.
Monopolistically competitive firms are most common in industries where differentiation is possible, such as:
- The restaurant business
- Hotels and pubs
- General medical specialist retailing
- Consumer services, such American Samoa hairdressing
The survival of the fittest of small firms
The existence of monopolistic competition partly explains the survival of bantam firms in Bodoni economies. The majority of small firms in the factual world operate in markets that could be same to be monopolistically competitive.
Evaluation
The advantages of noncompetitive competition
Monopolistic competition can bring the next advantages:
- There are nobelium significant barriers to entry; therefore markets are relatively shakeable.
- Differentiation creates variety, choice and utility. For deterrent example, a normal high schoo street in some town leave let a number of variant restaurants from which to choose.
- The market is more efficient than monopoly but to a lesser extent efficient than perfect rival – less allocatively and less productively efficient. However, they may be dynamically underspent, innovative in damage of new yield processes or new products. For example, retailers often constantly have to develop new slipway to attract and retain local usance.
The disadvantages of noncompetitive contender
There are several potential disadvantages associated with monopolistic contender, including:
- Some specialisation does not create utility simply generates unnecessary waste, such equally excess publicity. Advertising Crataegus oxycantha also be considered wasteful, though nearly is informative rather than persuasive.
- Every bit the diagram illustrates, assuming net profit maximisation, there is allocative inefficiency in some the endless and truncate course. This is because price is above fringy cost in both cases. In the yearn run the firm is less allocatively inefficient, but it is tranquillise inefficient.
Inefficiency
The firm is allocatively and productively ineffectual in both the long and short run.

There is a tendency for excess capacity because firms backside never amply exploit their fixed factors because mass production is difficult. This means they are productively inefficient in some the extended and short run. However, this is may be outweighed by the advantages of diversity and choice.
As an economic model of rival, monopolistic competition is more realistic than perfect competition – many another familiar and commonplace markets throw many of the characteristics of this model.
Test your knowledge with a quiz
Fight Next to launch the quiz
You are allowed two attempts – feedback is provided after
each enquiry is attempted.
In the Long Run, Monopolistically Competitive Firms Produce Where Demand Equals Marginal Cost.
Source: https://www.economicsonline.co.uk/business_economics/monopolistic_competition.html/
0 Response to "In the Long Run, Monopolistically Competitive Firms Produce Where Demand Equals Marginal Cost."
Postar um comentário